High performance computing (HPC) is the ability to process data and perform complex calculations at high speeds. One of the best-known types of HPC solutions is the supercomputer. A supercomputer contains thousands of compute nodes that work together to complete one or more tasks. This is called parallel processing. HPC solutions have three main components: Compute , Network and Storage. To build a high performance computing architecture, compute servers are networked together into a cluster. Software programs and algorithms are run simultaneously on the servers in the cluster. The cluster is networked to the data storage to capture the output. Together, these components operate seamlessly to complete a diverse set of tasks.
To operate at maximum performance, each component must keep pace with the others. For example, the storage component must be able to feed and ingest data to and from the compute servers as quickly as it is processed. Likewise, the networking components must be able to support the high-speed transportation of data between compute servers and the data storage. If one component cannot keep up with the rest, the performance of the entire HPC infrastructure suffers.
Containers give HPC the portability that Hybrid Cloud demands .Containers are ready-to-execute packages of software. Container technology provides hardware abstraction, wherein the container is not tightly coupled with the server. Abstraction between the hardware and software stacks provides ease of access, ease of use, and the agility that bare metal environments lack.
 |
| Source |
Software containers and Kubernetes are important tools for building, deploying, running and managing modern enterprise applications at scale and delivering enterprise software faster and more reliably to the end user while using resources more efficiently and reducing costs. Recently, high performance computing (HPC) is moving closer to the enterprise and can therefore benefit from an HPC container and Kubernetes ecosystem, with new requirements to quickly allocate and deallocate computational resources to HPC workloads so that planning of compute capacity no longer required in advance. The HPC community is picking up the concept and applying it to batch jobs and interactive applications.
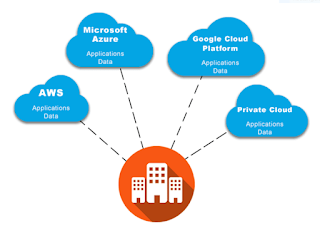
In a multi-cloud environment, an enterprise utilizes multiple public cloud services, most often from different cloud providers. For example, an organization might host its web front-end application on AWS and host its Exchange servers on Microsoft Azure. Since all cloud providers are not created equal, organizations adopt a multi-cloud strategy to deliver best of breed IT services, to prevent lock-in to a single cloud provider, or to take advantages of cloud arbitrage and choose providers for specific services based on which provider is offering the lowest price at that time. Although it is similar to a hybrid cloud, multi-cloud specifically indicates more than one public cloud provider service and need not include a private cloud component at all. Enterprises adopt a multi-cloud strategy so as not to ‘keep all their eggs in a single basket’, for geographic or regulatory governance demands, for business continuity, or to take advantage of features specific to a particular provider.
 |
| source |
Multi-cloud is the use of multiple cloud computing and storage services in a single network architecture. This refers to the distribution of cloud assets, software, applications, and more across several cloud environments. With a typical multi-cloud architecture utilizing two or more public clouds as well as private clouds, a multi-cloud environment aims to eliminate the reliance on any single cloud provider or instance.
Multi-cloud is the use of two or more cloud computing services from any number of different cloud vendors. A multi-cloud environment could be all-private, all-public or a combination of both. Companies use multi-cloud environments to distribute computing resources and minimize the risk of downtime and data loss. They can also increase the computing power and storage available to a business. Innovations in the cloud in recent years have resulted in a move from single-user private clouds to multi-tenant public clouds and hybrid clouds — a heterogeneous environment that leverages different infrastructure environments like the private and public cloud.
A multi-cloud platform combines the best services that each platform offers. This allows companies to customize an infrastructure that is specific to their business goals. A multi-cloud architecture also provides lower risk. If one web service host fails, a business can continue to operate with other platforms in a multi-cloud environment versus storing all data in one place. Examples of public Cloud Providers:
- IBM Cloud [https://www.ibm.com/cloud]
- AWS [https://aws.amazon.com/]
- Microsoft Azure [https://azure.microsoft.com/en-us/free/]
- Google Cloud Platform [https://cloud.google.com/]
- Openstack (private cloud)
- Rackspace
- VMware Cloud
Hybrid-cloud A hybrid cloud architecture is mix of on-premises, private, and public cloud services with orchestration between the cloud platforms. Hybrid cloud management involves unique entities that are managed as one across all environments. Hybrid cloud architecture allows an enterprise to move data and applications between private and public environments based on business and compliance requirements. For example, customer data can live in a private environment. But heavy processing can be sent to the public cloud without ever having customer data leave the private environment. Hybrid cloud computing allows instant transfer of information between environments, allowing enterprises to experience the benefits of both environments.
Hybrid cloud architecture works well for the following industries:
• Finance: Financial firms are able to significantly reduce their space requirements in a hybrid cloud architecture when trade orders are placed on a private cloud and trade analytics live on a public cloud.
• Healthcare: When hospitals send patient data to insurance providers, hybrid cloud computing ensures HIPAA compliance.
• Legal: Hybrid cloud security allows encrypted data to live off-site in a public cloud while connected o a law firm’s private cloud. This protects original documents from threat of theft or loss by natural disaster.
• Retail: Hybrid cloud computing helps companies process resource-intensive sales data and analytics.
The hybrid cloud strategy could be applied to move workloads dynamically to the most appropriate IT environment based on cost, performance and security. Utilize on-premises resources for existing workloads, and use public or hosted clouds for new workloads. Run internal business systems and data on premises while customer-facing systems run on infrastructure as a service (iaaS), public or hosted clouds.
Reference:
https://www.hpcwire.com/2019/09/19/kubernetes-containers-and-hpc
https://www.hpcwire.com/2020/03/19/kubernetes-and-hpc-applications-in-hybrid-cloud-environments-part-ii
https://www.hpcwire.com/2021/09/02/kubernetes-based-hpc-clusters-in-azure-and-google-cloud-multi-cloud-environment
https://www-stage.avinetworks.com/
https://www.vmware.com/topics/glossary/content/hybrid-cloud-vs-multi-cloud